The cybersecurity landscape has witnessed a dramatic transformation in social engineering attacks from 2024 to 2025, characterized by unprecedented growth in AI-powered threats and a fundamental shift in attack methodologies. This comprehensive analysis reveals critical trends that organizations must understand to defend against increasingly sophisticated human-targeted cyber threats.
Social engineering remains the most prevalent attack vector in cybersecurity, accounting for 60% of all data breaches that involve human manipulation. However, the nature of these attacks has evolved dramatically, with AI-powered methods showing explosive growth while traditional approaches become more targeted and sophisticated.
Overall Threat Landscape
The global social engineering threat reached alarming proportions in 2024, with nearly 1 million phishing attacks recorded worldwide in Q4 2024 alone, representing a 100,000-attack increase from the previous quarter. Despite a 20% global decrease in overall phishing volume, attacks have become significantly more targeted and effective.
Financial Impact
The economic consequences of social engineering attacks reached staggering levels in 2024:
- $12.5 billion in fraud-related losses reported by U.S. consumers alone.
- $2.77 billion in Business Email Compromise (BEC) losses.
- Average data breach cost of $4.88 million, with phishing-related breaches among the most expensive.
- $130,000 average cost per social engineering attack.
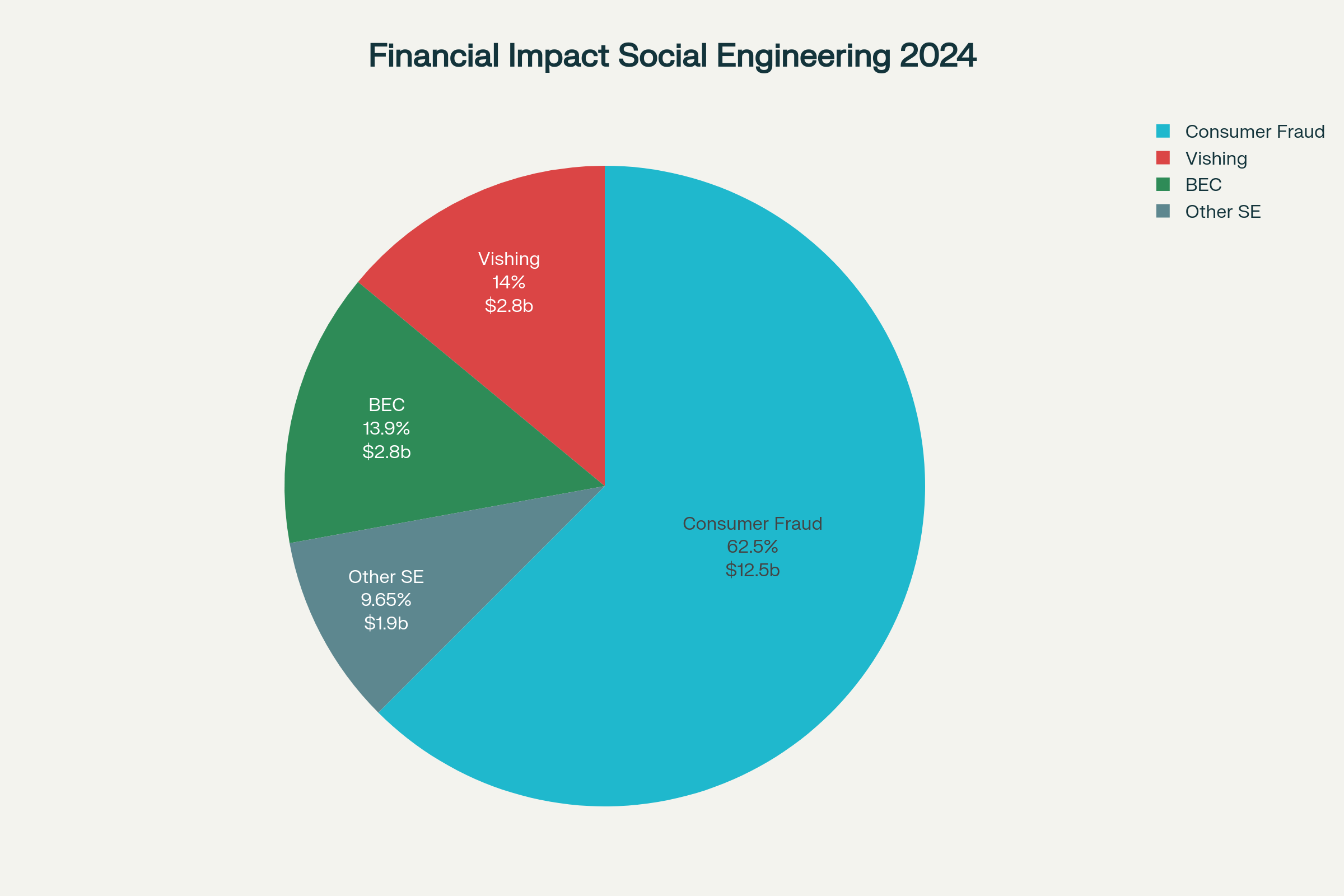
Figure 1: Distribution of financial losses from different types of social engineering attacks in 2024, totaling approximately $20 billion in reported losses.
Attack Type Analysis
1. AI-Generated Phishing – The New Frontier
The integration of artificial intelligence into phishing campaigns represents the most significant evolution in social engineering. AI-generated phishing emails achieved a 54% click-through rate compared to just 12% for human-written messages. Since the launch of ChatGPT, phishing email volume has surged by 1,265%, with 73.8% of phishing emails analyzed in 2024 utilizing some form of AI.
2. Voice Phishing (Vishing) – Explosive Growth
Vishing attacks experienced unprecedented growth, with a 442% increase from the first to second half of 2024. This surge is attributed to attackers exploiting the trust inherent in voice communications, with 6.5% of employees revealing sensitive information to fake vishing calls. The average annual cost of vishing attacks reaches $14 million per organization.
3. Business Email Compromise (BEC) – Persistent Threat
BEC attacks continue to be financially devastating, showing a 30% increase as of March 2025. These attacks now account for 73% of all cyber incidents in 2024, with the average wire transfer request valued at $24,586. Notably, 40% of BEC emails were found to be AI-generated, demonstrating the convergence of traditional and AI-powered attack methods.
4. Deepfake Attacks – Sophisticated Deception
Deepfake technology has emerged as a game-changing threat, with incidents increasing 10-fold globally from 2022 to 2023. In North America, deepfake fraud rose by 1,740% in 2023. These attacks occur with alarming frequency – every 5 minutes globally by 2024. The sophistication is evident in high-profile cases like the $25 million Arup attack, where employees were deceived during a video conference with AI-generated deepfakes of company executives.
5. SMS Phishing (Smishing) – Mobile Vulnerability
Smishing attacks have shown consistent growth, with a 22% increase in Q3 2024. In 2023, 75% of organisations experienced smishing attacks, which now account for 45% of mobile threats. Americans received a record 19.2 billion spam text messages in February 2025.
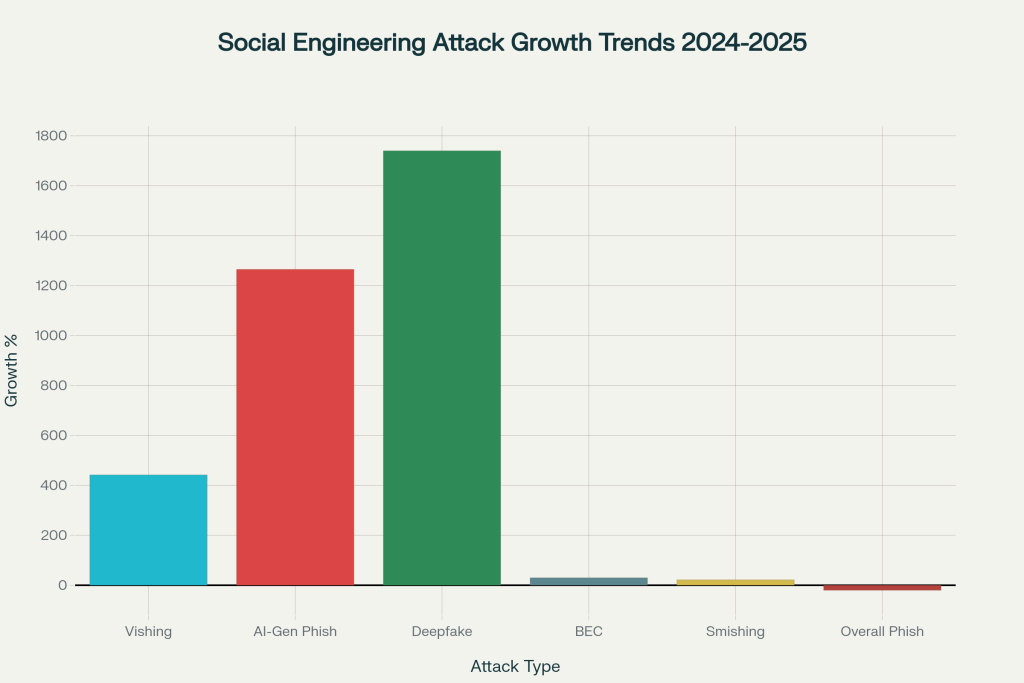
Figure 2: Growth trends of major social engineering attack types showing dramatic increases in AI-powered and voice-based attacks during 2024-2025
Success Rates and Detection Challenges
The research reveals concerning success rates across different attack vectors:
- Deepfake attacks: 95% success rate.
- Smishing: 75% organizational impact.
- BEC attacks: 73% of cyber incidents.
- Spear phishing: 66% of breaches despite being only 0.1% of attacks.
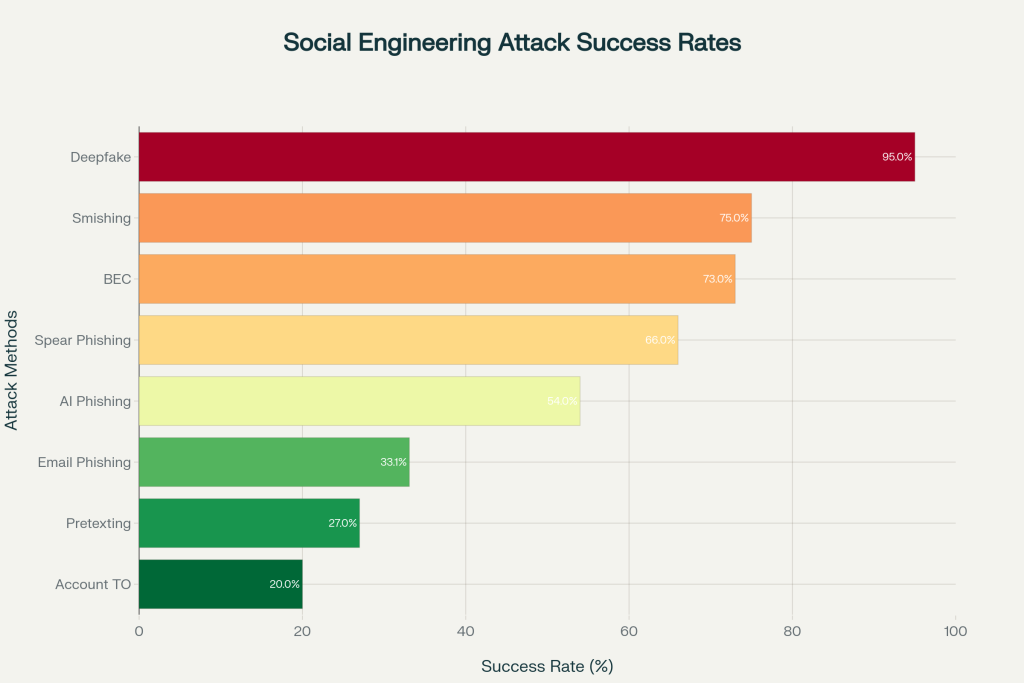
Figure 3: Success rates of different social engineering attack methods, showing deepfake attacks having the highest success rate at 95%.
The median time for victims to respond to phishing emails is less than 60 seconds, with users taking just 21 seconds to click malicious links and another 28 seconds to provide requested information. AI-powered attacks present unprecedented detection challenges. AI detectors cannot distinguish AI-generated phishing emails from human-written ones in 74% of cases. This detection gap is particularly concerning given that 98% of cyberattacks rely on social engineering tactics.
Industry and Geographic Impacts
Small businesses face disproportionate risk, being targeted nearly 4 times more often than their larger counterparts. In 2024, 94% of small businesses were attacked, up from 73% the previous year. Even organizations with fewer than 1,000 employees have a 70% chance of experiencing at least one BEC attempt weekly. Geographically, the United States experiences the highest number of phishing attacks globally, accounting for 34.89% of incidents, though attacks decreased by 32% in the U.S. in 2024.
Industry-Specific Vulnerabilities
Research identified the most vulnerable sectors:
- Healthcare & Pharmaceuticals: 41.9% vulnerability rate
- Insurance: 39.2% vulnerability rate
- Retail & Wholesale: 36.5% vulnerability rate
The healthcare sector was particularly impacted, with 389 healthcare institutions hit by ransomware between 2023 and 2024.
Emerging Technologies and Future Threats
The convergence of multiple technologies is creating new attack vectors:
- Voice cloning technology requires only 10 minutes of recorded speech to achieve a convincing impersonation.
- Synthetic voice fraud risk is rising 475% in 2024 within the insurance industry.
- Automated calling systems are conducting thousands of simultaneous, personalized calls.
- Deepfake video technology enables real-time impersonation during video conferences.
Recommendations for Organizations
Based on the research findings, organizations should prioritize:
- AI-aware security training that addresses the sophistication of modern attacks.
- Multi-layered verification processes for financial transactions and sensitive requests.
- Voice authentication alternatives have given rise to deepfake voice cloning.
- Enhanced mobile security measures to combat smishing attacks.
- Regular simulation exercise,s including vishing and deepfake scenarios.
Conclusion
The state of social engineering in 2024-2025 represents a paradigm shift in cybersecurity threats. The explosive growth of AI-powered attacks, particularly deepfakes and automated phishing, combined with the persistent effectiveness of traditional methods like BEC, creates an unprecedented challenge for organizations worldwide. With $20+ billion in documented losses and attack success rates reaching 95% for sophisticated methods, social engineering has evolved from a peripheral concern to the primary battleground in cybersecurity.
Organizations must recognize that the human element remains the most vulnerable aspect of their security posture, requiring comprehensive, technology-aware training programs and robust verification procedures to combat increasingly sophisticated social engineering campaigns.

